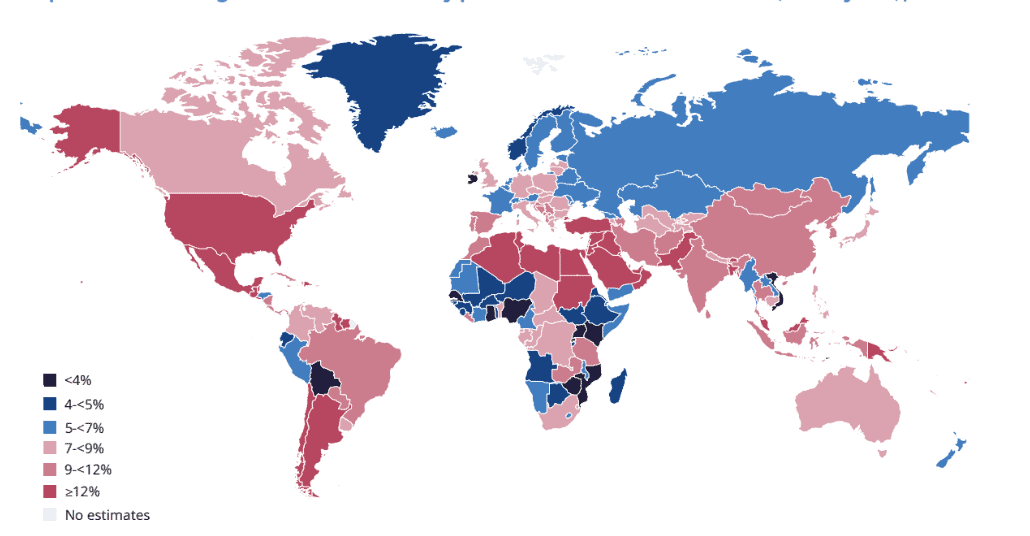
The number of adults living with diabetes has more than doubled over the span of 30 years, rising from 7% in 1990 to more than 14% in 2022. An estimated 828 million adults worldwide currently live with diabetes, and if trends continue, this is projected to reach 1.3 billion by 2050.
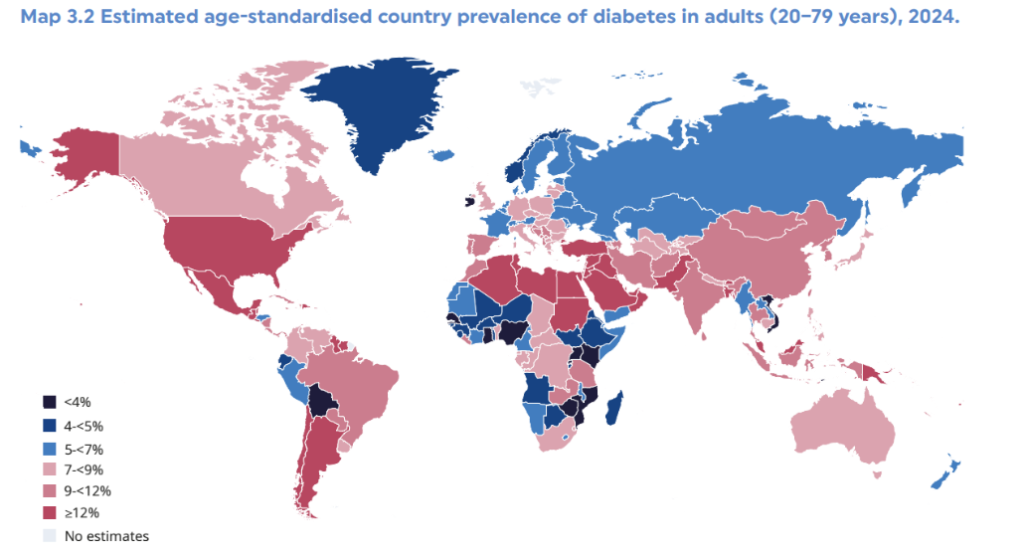
Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs when the body is unable to produce enough insulin – a hormone which regulates blood sugar – or unable to efficiently use the insulin it produces. This condition leads to high blood sugar levels, which, if left untreated, can result in severe health complications such as blindness, nerve damage, heart disease, kidney failure, and obesity. Early intervention, including lifestyle and dietary changes, can help prevent and manage diabetes effectively.
Why Should Employers Care?
The surge in diabetes extends far beyond public health concerns, significantly impacting business performance and economic stability. Alongside the direct costs related to diabetes care and treatment, the hidden indirect costs, such as lost productivity, absenteeism, and presenteeism, place a heavy economic burden on businesses across all sectors. In the United States, where 11% of the population is affected by diabetes, the annual cost of diagnosed diabetes reaches up to $250 billion, with $70 billion attributed to indirect costs such as lost productivity. Click here to read more.